Dove Imagery used to Assess Economic Damage after a Wildfire in Haifa, Israel
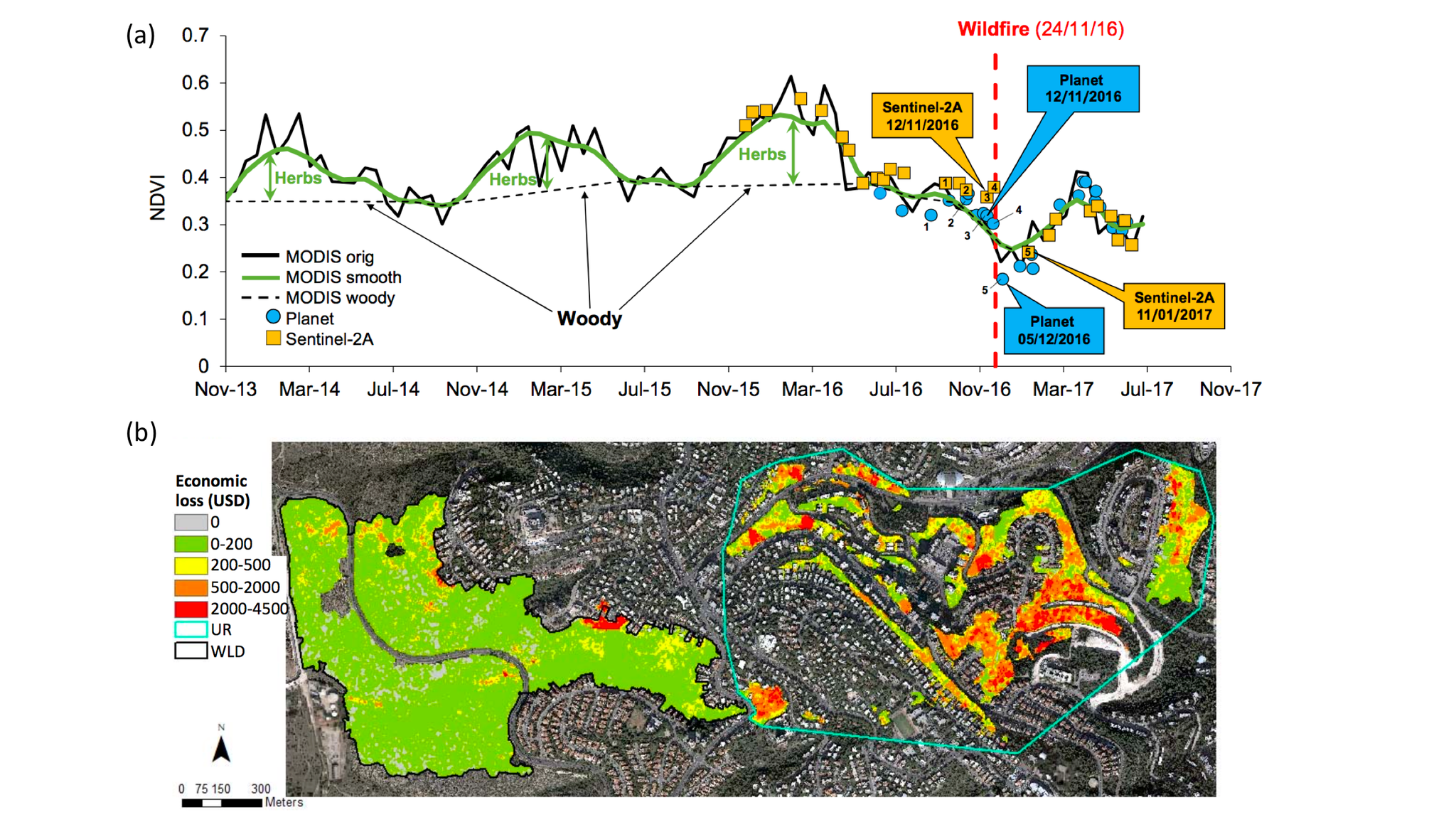
In November, 2016, Haifa, Israel experienced a fire on the Wildland-Urban Interface (WUI), causing damage to homes and other infrastructure in the urban forest landscape. The damage was visible in several Earth Observation datasets, including MODIS, Sentinel-2, and the Planet Dove constellation. Yaron Michael, in the Department of Geography and Environment at Bar-Ilan University, leveraged Planet’s Dove data to conduct a post-fire economic assessment. Michael and his team created fire severity maps from Dove imagery, which were validated at 87% overall accuracy based on field surveys. By incorporating the public value of urban trees, Michael and team concluded that the fire resulted in $41M (+/- 10) USD in damages to the urban forest. With the high spatial resolution available in Dove data, they were able to produce pixel-level damage assessment. Michael and team conclude: “ ...images acquired from the high-spatial-resolution Planet Doves database may be used to derive tree parameters such as stand density and DBH using simple vegetation indices. It also shows that burn severity mapping may be conducted using Planet images in the complex WUI area.” The full paper is available via open access from the journal Remote Sensing. [caption id="attachment_142900" align="aligncenter" width="2451"]

Ready to Get Started
Connect with a member of our Sales team. We'll help you find the right products and pricing for your needs